
Protect Your Java, Kotlin and Android Applications
Obfuscation is much more than just renaming! Only a layered obfuscation approach can provide the protection you need. Review each section below to learn more.
• Tamper Detection & Defense • Debug Detection & Defense Using Checks
• Root Check For Android • Emulator Check For Android
• Hooking Check For Android • Shelf Life
RENAMING
Renaming alters the names of methods, variables, etc., making source code more difficult to understand. DashO uses a deeper form of obfuscation, patented by PreEmptive Solutions, called Overload Induction™. Instead of substituting one new name for each old name, Overload Induction renames as many methods as possible to the same name. After this deep obfuscation, the logic, while not destroyed, is beyond comprehension. The following simple example illustrates the power of the Overload Induction technique:
| Original Source Code Before Obfuscation | Reverse-Engineered Source Code After Overload Induction Obfuscation |
|---|---|
private void CalcPayroll (SpecialList employeeGroup) { while(employeeGroup.HasMore()) { employee = employeeGroup.GetNext(true); employee.UpdateSalary(); DistributeCheck(employee); } } |
private void a(a b) { while (b.a()) { a = b.a(true); a.a(); a(a); } } |
CONTROL FLOW
Traditional control flow obfuscation introduces false conditional statements and other misleading constructs in order to confuse and break decompilers. This process synthesizes branching, conditional, and iterative constructs that produce valid forward (executable) logic, but yield non-deterministic semantic results when decompilation is attempted. Control Flow obfuscation produces spaghetti logic that can be very difficult for a cracker to analyze.
DashO employs advanced control flow obfuscation. In addition to adding code constructs, DashO works by destroying the code patterns that decompilers use to recreate source code. The end result is code that is semantically equivalent to the original but contains no clues as to how the code was originally written. Even if highly advanced decompilers are developed, their output will be guesswork.
| Original Source Code Before Obfuscation | Reverse-Engineered Source Code After Control Flow Obfuscation |
|---|---|
public int CompareTo(Object o) { int n = occurrences – ((WordOccurrence)o).occurrences; if (n == 0) { n = String.Compare(word,((WordOccurrence)o).word); } return(n); } |
public virtual int _a(Object A_0) { int local0; int local1; local 10 = this.a – (c) A_0.a; if (local0 != 0) goto i0; while (true) { return local1; i0: local1 = local10; } i1: local10 = System.String.Compare(this.b, (c) A_0.b); goto i0; } |
STRING ENCRYPTION
DashO allows you to hide user strings that are present in your binaries. A common attacker technique is to locate critical code sections by looking for string references inside the binary. For example, if your application is time locked, it may display a message when the timeout expires. Attackers search for this message inside the disassembled or decompiled output and chances are when they find it, they will be very close to your sensitive time lock algorithm.
DashO addresses this problem by allowing you to encrypt strings in these sensitive parts of your application, providing an effective barrier against this type of attack.
RESOURCE ENCRYPTION
DashO allows you to protect the resources included in your application’s APK. This makes it much harder for attackers to inspect, copy, or alter them. DashO encrypts these resources and injects code to decrypt them as the application runs.
WATERMARKING
Watermarking helps track unauthorized copies of your software back to the source by embedding data such as copyright information or unique identification numbers into an application without impacting its runtime behavior. DashO’s watermarking algorithm does not increase the size of your application, nor does it introduce extra metadata that could break your application.
REMOVAL
Small applications download faster, install faster, load faster and run faster. DashO's pruning feature statically analyzes your code to find the unused types, methods, and fields, and removes them, making the application smaller and reducing the data available to an attacker. DashO can also remove used methods like debugging and logging calls, that aren’t wanted in released applications.
TAMPER DETECTION & DEFENSE
DashO injects code that verifies your application’s integrity at runtime. If it detects tampering, it can shut down the application, invoke random crashes (to disguise that the crash was the result of a tamper check), or perform any other custom action.
DEBUG DETECTION & DEFENSE USING CHECKS
Checks are prebuilt validations DashO can inject into your Java and Android apps. Your apps will then be able to detect unauthorized use, like debugging or tampering. Despite the name, Checks do more than just detect these states; they can also react in pre-specified ways, such as by exiting the app. Checks can also call into application code, allowing for custom behavior based on the Check’s result. These reporting and response features are configurable per-Check, so all your apps can detect unauthorized uses in the same way, but each app can respond to that detection differently.
ROOT CHECK FOR ANDROID
Rooted devices are an important security concern for your Android apps. DashO can detect when an app is running on a rooted device (offline or on a network) and users can abort the session, quarantine the app, and/or report the incident.
EMULATOR CHECK FOR ANDROID
With DashO, you can tell your application to shut down or behave differently when it is run inside an emulator. This prevents attackers from probing the application's defenses under emulation.
HOOKING CHECK FOR ANDROID
Hackers use hooking frameworks to inspect and change the application at runtime, without modifying the binaries. DashO can detect the presence of hooking frameworks in the environment. The app can respond accordingly (e.g. by shutting down, throwing an exception or hanging, sending an alert, etc.).
SHELF LIFE
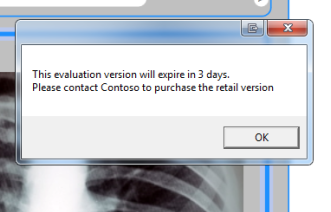
Shelf Life is an application inventory management function that allows you to embed expiration, or deactivate, and notification logic into an application. DashO injects code that reacts to application expiration by exiting the application. This feature is particularly helpful with beta or evaluation applications. Users can schedule an application’s expiration/de-activation for a specific date and optionally issue warnings to users that the application will expire/de-activate in a specific number of days.

